Definition of Critical Thinking
Critical thinking is the mental process of carefully evaluating information and determining how to interpret it to make a sound judgment.
About Critical Thinking
Critical thinking employs logic and reasoning to come to a conclusion about how best to perceive and interpret information in order to make sound judgments.
With this type of thinking, you make conclusions regarding your unique perception of the information. You investigate other pieces of data that could be relevant. Then you combine your new information with your existing knowledge of the world to make the most accurate assessment. Essentially, you reflect upon information in order to form a sound judgment that reconciles scientific evidence with common sense.
Ultimately, you make reasoned judgments that are logical and well thought out by assessing the evidence that supports a specific theory or conclusion.
Steps for Critical Thinking
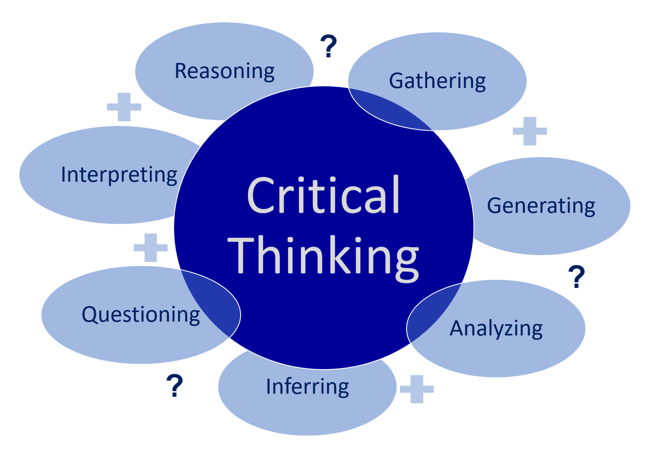
Critical thinking involves gathering all relevant information, then evaluating the information to determine how it should be best interpreted. You evaluate information by asking questions, assessing value, and making inferences. You then formulate ideas and theories based on the evaluation. You consider outside information rather than sticking strictly with the information presented. You then consider alternative possibilities before reaching a well-reasoned conclusion. Finally, you test your conclusions in an attempt to verify if evidence supports your conclusions and make your judgment.
Critical thinking involves:
- Gathering relevant information
- Evaluating information
- Asking questions
- Assessing bias or unsubstantiated assumptions
- Making inferences from the information and filling in gaps
- Using abstract ideas to interpret information
- Formulating ideas
- Weighing opinions
- Reaching well-reasoned conclusions
- Considering alternative possibilities
- Testing conclusions
- Verifying if evidence/argument support the conclusions